What is Java?
Developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995, Java is a highly popular, object-oriented programming language. This platform independent programming language is utilized for Android development, web development, artificial intelligence, cloud applications, and much more.
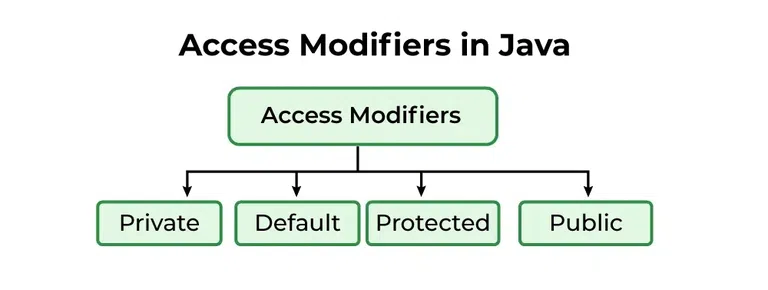
Basic terminologies in Java
Class:The class is a blueprint (plan) of the instance of a class (object). It can be defined as a logical template that share common properties and methods.
Object:The object is an instance of a class. It is an entity that has behavior and state.
Method:The behavior of an object is the method.
Instance variables:Every object has its own unique set of instance variables. The state of an object is generally created by the values that are assigned to these instance variables.
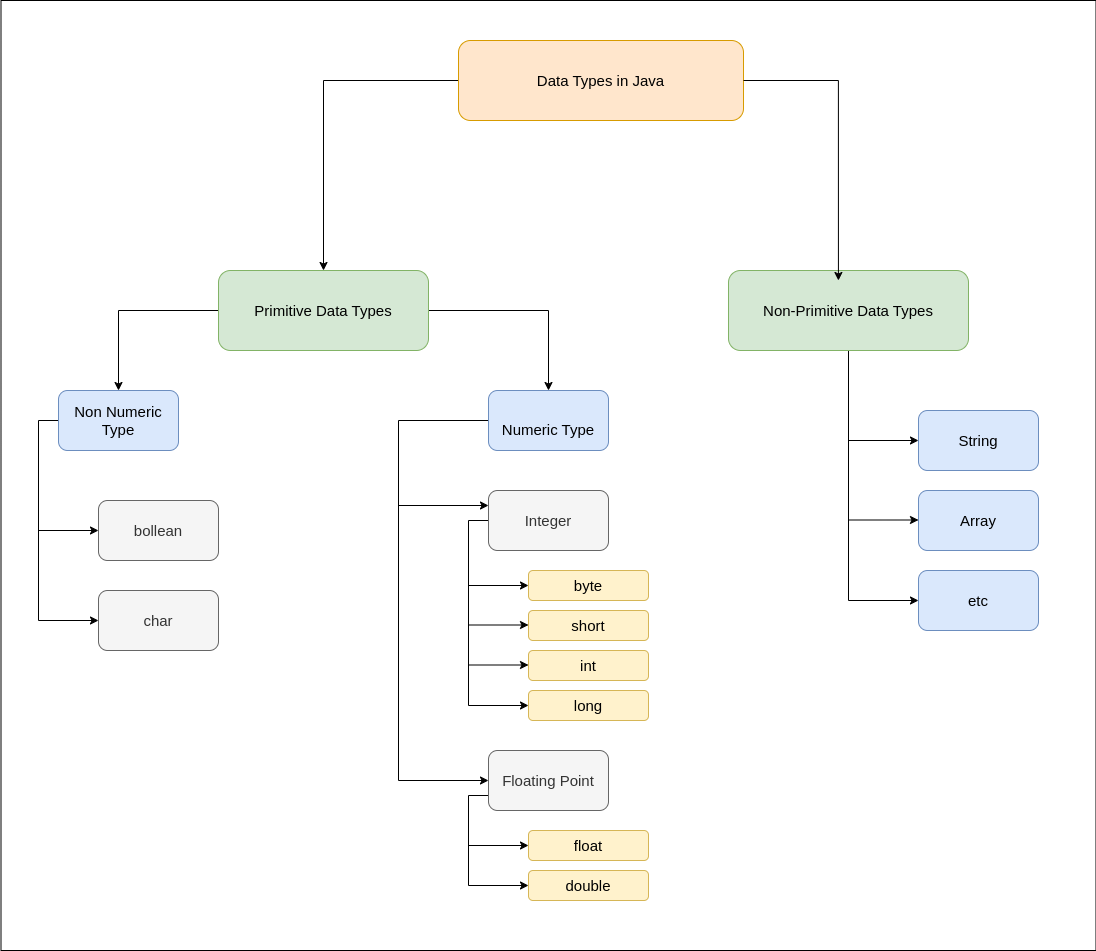
Java Data Types
Java has two categories in which data types are segregated
1.Primitive Data Type: such as boolean, char, int, short, byte, long, float, and double
2.Non-Primitive Data Type or Object Data type: such as String, Array, etc.
Operators in Java
Operators in Java are the symbols used for performing specific operations in Java. Operators make tasks like addition, multiplication, etc which look easy although the implementation of these tasks is quite complex.
| Class | Object |
|---|---|
| Class is the blueprint of an object. It is used to create objects. | An object is an instance of the class. |
| No memory is allocated when a class is declared. | Memory is allocated as soon as an object is created. |
| A class is a group of similar objects. | An object is a real-world entity such as a book, car, etc. |
| Class is a logical entity. | An object is a physical entity. |
| A class can only be declared once. | Objects can be created many times as per requirement. |
| An example of class can be a car. | Objects of the class car can be BMW, Mercedes, Ferrari, etc. |